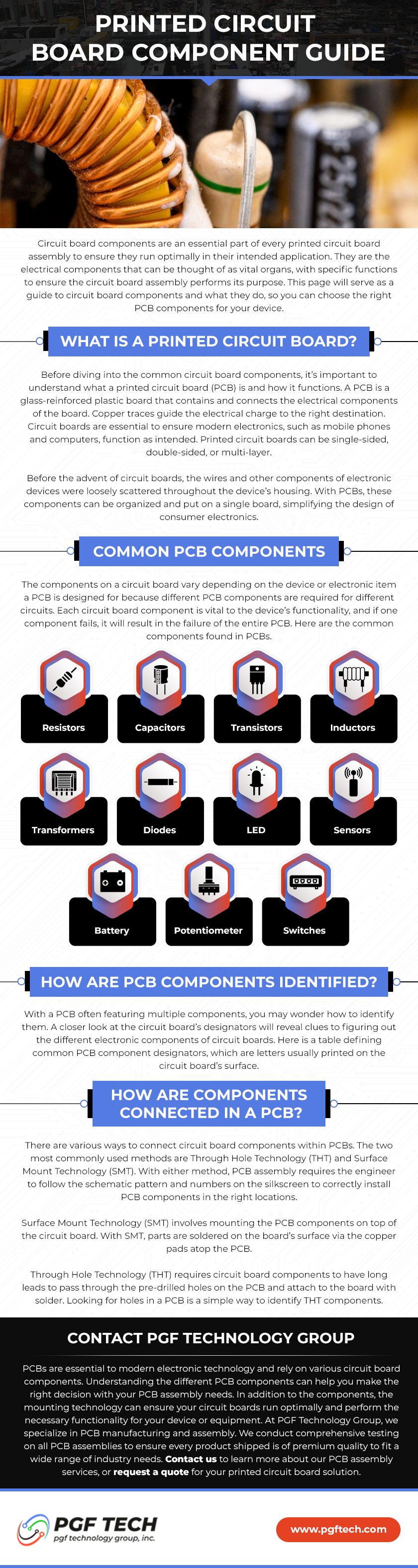
PCBA Layers: Understanding the Fundamentals
| By Momentum | 0 Comments

PCBAs are like Onions
Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCBAs) are a crucial component in the functioning of electronic devices. These boards have multiple layers, each playing a critical role in the performance and reliability of the electronic assembly. In this blog post, we will discuss the PCBA layers and what they contribute to the functioning of electronic devices.
Peel Back the Layers
A typical PCBA has several layers, including the substrate, conductive layers, and insulating layers. The substrate is the base material of the PCB. It is usually made of fiberglass or other composite materials and provides mechanical support for the other components. The conductive layers, typically copper, carry electrical signals and form electrical pathways that connect various components. Insulating layers, made from a dielectric material, provide insulation between conductive layers and prevent electrical cross-talk between pathways.
How Many Layers?
The number of layers in a PCB can vary, but most PCBs consist of four to six layers. The layer count and layout of a PCB are critical factors in the design of electronic devices. They require specialized knowledge and experience to ensure optimal performance and reliability. For example, the surface layer of a PCB is usually for surface mount components, while internal layers are for routing or shielding.
Benefits of Working with an EMS Provider
Extensive Experience
A benefit of an experienced EMS provider is their ability to assemble PCBAs with optimized layer counts and layouts. PGF Technology Group has extensive experience in PCBAs and uses the latest techniques to deliver high-quality and reliable products.
Cost-Effective
In addition to the quality of the manufacturing process, experienced electronics manufacturing service providers like PGF Technology Group can also provide efficient and cost-effective solutions. Our manufacturing process minimizes waste, reduces the risk of defects, and maximizes production efficiency. Our team of engineers and technicians use advanced techniques, such as real-time process monitoring and control, to ensure projects are on time and within budget.
Total Solution
Another advantage of working with an experienced electronics manufacturing service provider is the ability to provide a complete solution for your PCB needs. Our experienced team can handle the entire process, from design to fabrication and assembly, allowing you to focus on your core business activities. We work closely with our customers to understand their requirements and deliver solutions that meet their specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the layers of a PCB play a critical role in the performance and reliability of electronic devices. A well-designed and manufactured PCB requires specialized knowledge and experience, and strict control of the manufacturing process. Working with an experienced electronics manufacturing service provider, like PGF, ensures the highest quality and reliability.
By understanding the different PCBA layers, you can better appreciate the importance of working with an experienced electronics manufacturing service provider. The team at PGF Technology Group would be happy to discuss your needs and provide a solution that meets your requirements.