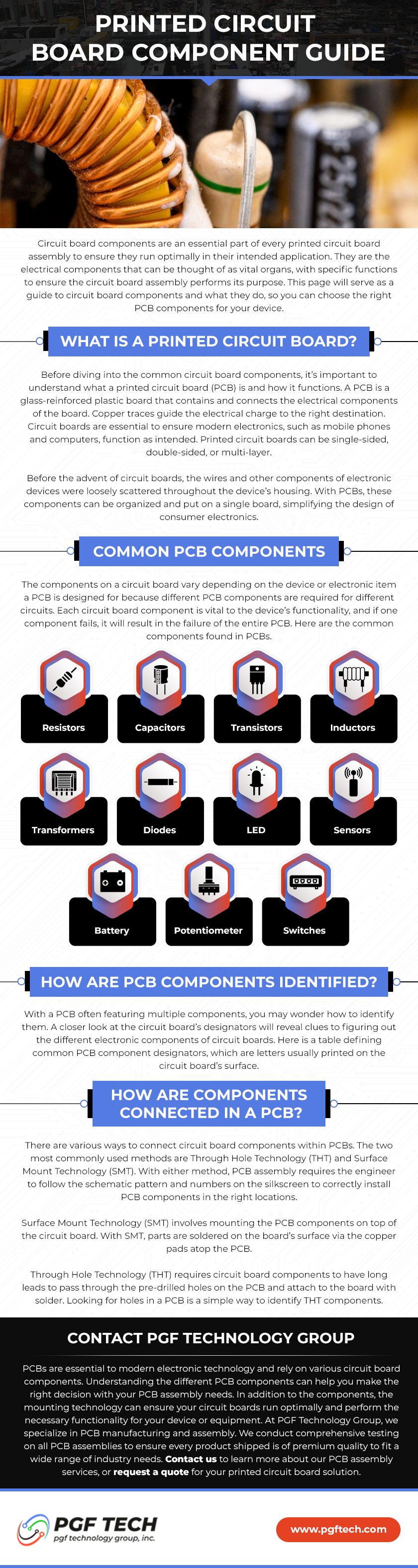
What’s the BGA Deal?
Printed circuit board (PCB) assembly has come a long way since the early days of through-hole components. With the advent of surface mount technology (SMT), components have become smaller and more densely packed, making PCB assembly more challenging. One type of component that has become increasingly popular in recent years is the ball grid array (BGA).
What is a BGA?
A BGA is a type of surface mount component that uses an array of solder balls to make contact with the PCB. The solder balls are arranged in a grid pattern on the bottom of the component and are typically made of lead-free solder. BGAs can have anywhere from a few dozen to several thousand solder balls, depending on the size and complexity of the component.
Why use BGAs?
BGAs have a number of advantages over other types of surface mount components. One of the biggest advantages is their high pin density. Because the solder balls are arranged in a grid pattern, BGAs can accommodate more pins in a smaller area than other types of components. This makes them ideal for use in high-density applications, such as microprocessors and other complex integrated circuits.
BGAs also have a number of mechanical advantages. Because the solder balls are evenly distributed across the bottom of the component, they provide more uniform stress distribution during thermal cycling. This makes BGAs less prone to solder joint failure than other types of components.
Challenges of BGA assembly
While BGAs have many advantages, they also pose some unique challenges during assembly. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that each solder ball makes good contact with the PCB. Because the solder balls are small and densely packed, it can be difficult to inspect them visually. This is where X-ray inspection comes in. X-ray inspection is a non-destructive way to inspect the solder joints and ensure that each ball has made good contact with the PCB.
Another challenge with BGA assembly is the need for precise placement. Because the solder balls are arranged in a grid pattern, the component must be placed on the PCB with a high degree of accuracy. This requires specialized equipment and skilled technicians who are familiar with the nuances of BGA assembly.
Finally, the rework of BGA components can be difficult. Because the solder balls are on the bottom of the component, it can be difficult to access them for rework. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove the entire component and replace it with a new one.
Tips for successful BGA assembly
If you’re working with BGAs, there are a few things you can do to ensure successful assembly:
- Use a high-quality solder paste with the correct viscosity and solder ball size
- Ensure that your pick-and-place machine is properly calibrated and can handle the size and weight of your BGA components
- Inspect your solder joints using X-ray or other non-destructive testing methods
- Train your technicians in the proper handling and placement of BGAs
- Use a rework station that is specifically designed for BGA rework, if possible
Conclusion
BGAs are a popular type of surface mount component that offer many advantages in terms of pin density and mechanical reliability. However, they also pose some unique challenges during assembly, including precise placement and the need for X-ray inspection. By following best practices and using specialized equipment and techniques, you can successfully incorporate BGAs into your PCBA designs.
To ensure greatness, utilize an experienced PCB Assembly manufacturer like PGF Technology Group. We use all of the latest technology to guarantee high-quality work.